What is the Strongest Area of the Head? Uncovering the Secrets of Skull Strength
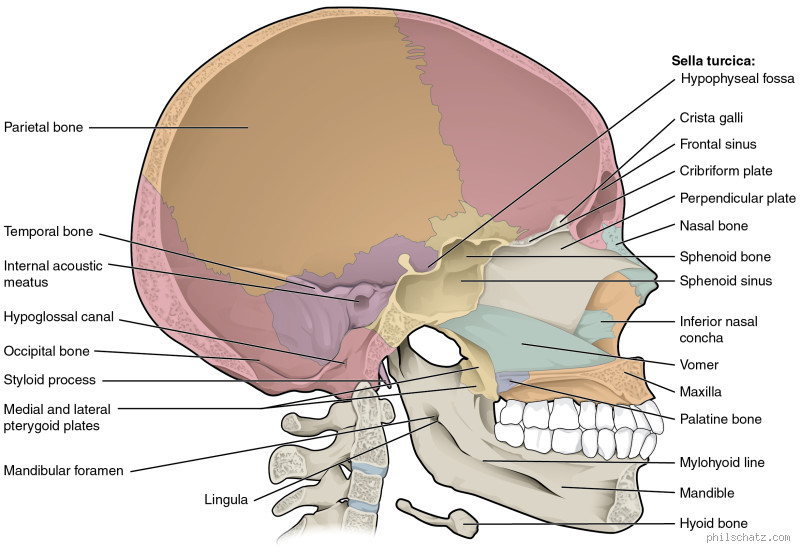
Understanding the Strength of the Skull
You’ve probably heard the phrase "tough as nails," but have you ever wondered about the strongest area of your head? The human skull is an incredibly resilient structure, protecting your brain and other vital organs from trauma. But what is the strongest area of the head, and why does it matter?
When I asked my friend Matt, who works in medicine, he pointed out something really interesting. "Your skull is stronger than you think, but there are specific areas that are more durable than others." That really got me thinking. So, let's take a deeper dive into the anatomy of the skull and figure out exactly what part of our head is the toughest.
The Anatomy of the Skull: Where is the Strength?
The Role of the Skull in Protection
The skull is made up of several bones that fuse together over time, forming a hard, protective shell for the brain. It's designed to absorb and distribute impacts, reducing the risk of serious injury. But not all parts of the skull are created equally—some areas are inherently stronger and more resistant to force.
I remember when I was younger, I used to think that the skull was just a rigid "helmet" for our brains. It wasn’t until I learned about its structural features that I understood how complex and protective it really is.
Key Areas of the Skull and Their Strength
There are several parts of the skull that come into play when considering strength. While the entire skull provides protection, there are certain areas that are particularly tough.
The Frontal Bone: The Forehead's Toughest Region
The frontal bone, which forms your forehead, is one of the strongest parts of the skull. It’s thick and flat, designed to absorb and deflect impacts that might otherwise reach the more sensitive parts of the brain. The frontal bone is key in protecting against head injuries, especially those from the front.
Interestingly, I had a conversation with my cousin, who’s a football player, and he once mentioned how often he has to take hits to the head during his games. “It’s the forehead that takes most of the hit,” he said. That made me realize how tough that part of our skull really is.
The Parietal Bones: The Sides of the Skull
The parietal bones are located on the sides of the skull, and while they’re slightly thinner than the frontal bone, they still provide a great deal of protection. These bones are more flexible than the frontal bone, which allows them to absorb impact and distribute force.
I once witnessed a minor car accident where someone was hit on the side of the head. Despite the impact, the person walked away with only a mild bruise. It was a stark reminder of how effective these bones are at cushioning blows.
The Occipital Bone: Protecting the Brainstem
The occipital bone is at the back of your head, and it plays a crucial role in protecting the brainstem, which controls essential functions like breathing and heart rate. This area is incredibly strong because it’s designed to shield one of the most important parts of your body from injury.
I remember once reading about a study where head trauma caused by rear-end collisions was a concern. The occipital bone was mentioned as an area that often absorbed the force from such impacts, showing how this region is specifically designed to protect life-sustaining functions.
Factors That Influence Skull Strength
Bone Density and Structure
Different people have different skull shapes and densities, which can affect how well certain areas protect against injury. Factors like age, genetics, and even lifestyle can influence the thickness and strength of the bones in your skull.
For example, young people tend to have denser bones compared to older individuals. This means that in youth, the skull tends to be better equipped to handle impact. Interestingly, bone density can be maintained and even improved with regular exercise, which is why athletes often have particularly strong skulls.
The Role of Diet and Nutrition
Another factor that can influence the strength of your skull is nutrition. Consuming adequate amounts of calcium and vitamin D helps in the development and maintenance of strong bones.
I recall having a conversation with my mom about how important calcium is, especially as we age. She pointed out how she made sure we all took calcium supplements when we were younger. It wasn’t until later that I understood how crucial these nutrients are for ensuring the strength of the bones in the head.
The Myth of the "Tough Skull"
Is the Skull Really Indestructible?
While the skull is undeniably strong, it’s important to remember that no part of the body is invincible. Trauma or accidents can still lead to serious injury, especially if the force is great enough. The strongest area of the head might protect you from everyday impacts, but severe trauma—such as in a car accident—can still cause damage.
There’s a myth that the skull is completely indestructible, but this is far from the truth. I had a friend, Luke, who was in a biking accident, and even though he was wearing a helmet, he still suffered a concussion. The skull is strong, but it's not impervious to extreme force.
Conclusion: Which Area of the Head is the Strongest?
So, what is the strongest area of the head? The frontal bone is the strongest and most protective region, followed by the parietal bones and the occipital bone. These areas are designed to absorb and distribute force, protecting the brain from injury.
However, it's important to understand that the skull’s strength depends on many factors, including bone density and nutrition. While it’s incredibly tough, it’s also important to take measures to protect it, like wearing helmets and being cautious during high-risk activities.
If you’ve ever wondered why certain parts of your head are built stronger than others, now you have the answer! Stay safe and take care of your skull—it's your most precious protector.
How much height should a boy have to look attractive?
Well, fellas, worry no more, because a new study has revealed 5ft 8in is the ideal height for a man. Dating app Badoo has revealed the most right-swiped heights based on their users aged 18 to 30.
Is 172 cm good for a man?
Yes it is. Average height of male in India is 166.3 cm (i.e. 5 ft 5.5 inches) while for female it is 152.6 cm (i.e. 5 ft) approximately. So, as far as your question is concerned, aforesaid height is above average in both cases.
Is 165 cm normal for a 15 year old?
The predicted height for a female, based on your parents heights, is 155 to 165cm. Most 15 year old girls are nearly done growing. I was too. It's a very normal height for a girl.
Is 160 cm too tall for a 12 year old?
How Tall Should a 12 Year Old Be? We can only speak to national average heights here in North America, whereby, a 12 year old girl would be between 137 cm to 162 cm tall (4-1/2 to 5-1/3 feet). A 12 year old boy should be between 137 cm to 160 cm tall (4-1/2 to 5-1/4 feet).
How tall is a average 15 year old?
Average Height to Weight for Teenage Boys - 13 to 20 Years
| Male Teens: 13 - 20 Years) | ||
|---|---|---|
| 14 Years | 112.0 lb. (50.8 kg) | 64.5" (163.8 cm) |
| 15 Years | 123.5 lb. (56.02 kg) | 67.0" (170.1 cm) |
| 16 Years | 134.0 lb. (60.78 kg) | 68.3" (173.4 cm) |
| 17 Years | 142.0 lb. (64.41 kg) | 69.0" (175.2 cm) |
How to get taller at 18?
Staying physically active is even more essential from childhood to grow and improve overall health. But taking it up even in adulthood can help you add a few inches to your height. Strength-building exercises, yoga, jumping rope, and biking all can help to increase your flexibility and grow a few inches taller.
Is 5.7 a good height for a 15 year old boy?
Generally speaking, the average height for 15 year olds girls is 62.9 inches (or 159.7 cm). On the other hand, teen boys at the age of 15 have a much higher average height, which is 67.0 inches (or 170.1 cm).
Can you grow between 16 and 18?
Most girls stop growing taller by age 14 or 15. However, after their early teenage growth spurt, boys continue gaining height at a gradual pace until around 18. Note that some kids will stop growing earlier and others may keep growing a year or two more.
Can you grow 1 cm after 17?
Even with a healthy diet, most people's height won't increase after age 18 to 20. The graph below shows the rate of growth from birth to age 20. As you can see, the growth lines fall to zero between ages 18 and 20 ( 7 , 8 ). The reason why your height stops increasing is your bones, specifically your growth plates.
