Who Colonised China? The Complex History of Foreign Influence
China’s Long History: Was It Ever Fully Colonized?
Actually, if you’ve ever wondered about the history of China’s interaction with foreign powers, you’re in for an interesting journey. Now, the first thing you should know is that China as a whole has never been fully colonized like many countries in Africa or the Americas. But, the history of foreign influence, invasions, and colonization attempts in China is far from simple. Many nations have sought to control or influence parts of China over the centuries, leading to a complex and often painful history.
In this article, I’ll break down the different powers that have exerted control over China throughout history and explain why, despite many attempts, it was never fully colonized in the same way other countries were.
The Age of Western Influence: The Opium Wars and the Unequal Treaties
The Opium Wars: Opening the Door to Foreign Powers
Honestly, this period is one of the most frustrating chapters of Chinese history. In the mid-19th century, Britain, along with other Western powers like France, managed to impose significant influence over China, but not through colonization in the traditional sense. Instead, they pushed China into signing Unequal Treaties that gave these foreign powers enormous economic and territorial control.
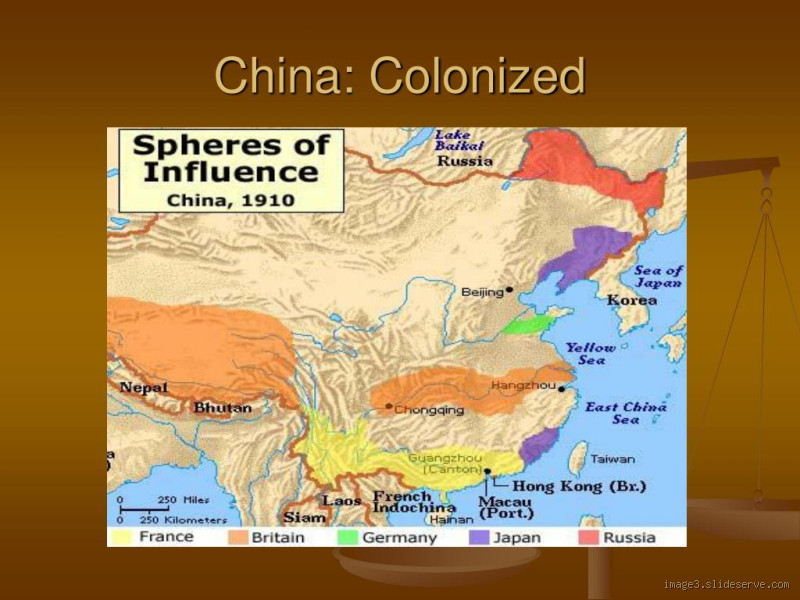
The Opium Wars (1839-1842 and 1856-1860) were a key moment. Britain, wanting to expand its trade, introduced opium into China, and when China tried to stop the opium trade, war broke out. The result? China lost both wars and was forced to open its ports to British trade, giving Britain control over important territories, including Hong Kong.
Hong Kong: A Legacy of Colonial Control
Hong Kong is probably the most famous legacy of British colonialism in China. The British controlled Hong Kong from 1842 until its handover in 1997. Even though Hong Kong’s status as a British colony is often referred to as a “semi-colonial” occupation, it’s a clear example of how China had to compromise in order to maintain some semblance of sovereignty.
I remember discussing with a friend who grew up in Hong Kong about how different the city felt when it was under British rule. It was a strange mix of British institutions combined with Chinese culture. She said it often felt like a blend of two worlds, and while it had its advantages, there were also tensions.
Japan’s Influence: The Japanese Occupation in the Early 20th Century
Japan’s Expansionist Ambitions: The Invasion of Manchuria
Well, another chapter of China's colonial history involves Japan. During the early 20th century, Japan, driven by imperial ambitions, invaded and occupied several parts of China, most notably Manchuria in 1931. Unlike the Western powers that only had a commercial grip on parts of China, Japan aimed at territorial domination, establishing the puppet state of Manchukuo.
The occupation during the Second Sino-Japanese War (1937-1945) was brutal, with horrific events like the Nanjing Massacre where hundreds of thousands of Chinese civilians were killed. Honestly, it’s hard not to feel the weight of such an invasion in the collective memory of the Chinese people.
The End of Japanese Occupation
Thankfully, Japan’s occupation ended after its defeat in World War II. However, Japan’s aggression left a deep scar on China. To this day, there are still tensions in the region, especially in places like the East China Sea where territorial disputes persist.
The Influence of Other Powers: Russia and the Qing Dynasty’s Decline
The Russian Empire’s Influence: A Battle for Land and Resources
Well, let’s not forget about the influence of Russia in the 19th century. While Russia did not colonize China in the traditional sense, it did gain significant control over regions in Central Asia and parts of Manchuria through treaties and military actions. The Treaty of Aigun (1858) and the Treaty of Tientsin (1858) gave Russia significant control over areas like Outer Manchuria, pushing back Chinese territory and deepening the pressure on the already weakening Qing Dynasty.
Honestly, the influence of Russia and the eventual encroachment by other Western powers was a huge factor in the decline of the Qing Dynasty, which had long struggled to maintain control over its vast empire.
The Legacy of Foreign Influence: Was China Ever Truly Colonized?
So, to answer the question: Who colonized China? While no one power ever fully colonized all of China, the country certainly faced overwhelming foreign influence, invasion, and territorial loss. The periods of Western imperialism and Japanese occupation in the 19th and 20th centuries were deeply impactful, but China, with its immense cultural and historical strength, never fully succumbed to colonization.
China’s modern rise can partly be attributed to its ability to reclaim sovereignty after these periods of foreign domination. The People’s Republic of China, founded in 1949, worked tirelessly to restore national pride and independence, after decades of suffering at the hands of foreign powers.
Conclusion: A Complex History of Foreign Influence
Honestly, when you look at the history, China’s story is one of resilience. It wasn’t colonized in the traditional sense like so many other nations, but it definitely faced intense foreign pressures, invasions, and loss of territory. The legacy of foreign influence has shaped modern China in ways that are still felt today.
In the end, the question of whether China was colonized is more complex than it appears. Multiple foreign powers sought to control parts of China, but the country’s strength and unity have ultimately allowed it to remain one of the most influential and proud nations in the world today.
How much height should a boy have to look attractive?
Well, fellas, worry no more, because a new study has revealed 5ft 8in is the ideal height for a man. Dating app Badoo has revealed the most right-swiped heights based on their users aged 18 to 30.
Is 172 cm good for a man?
Yes it is. Average height of male in India is 166.3 cm (i.e. 5 ft 5.5 inches) while for female it is 152.6 cm (i.e. 5 ft) approximately. So, as far as your question is concerned, aforesaid height is above average in both cases.
Is 165 cm normal for a 15 year old?
The predicted height for a female, based on your parents heights, is 155 to 165cm. Most 15 year old girls are nearly done growing. I was too. It's a very normal height for a girl.
Is 160 cm too tall for a 12 year old?
How Tall Should a 12 Year Old Be? We can only speak to national average heights here in North America, whereby, a 12 year old girl would be between 137 cm to 162 cm tall (4-1/2 to 5-1/3 feet). A 12 year old boy should be between 137 cm to 160 cm tall (4-1/2 to 5-1/4 feet).
How tall is a average 15 year old?
Average Height to Weight for Teenage Boys - 13 to 20 Years
| Male Teens: 13 - 20 Years) | ||
|---|---|---|
| 14 Years | 112.0 lb. (50.8 kg) | 64.5" (163.8 cm) |
| 15 Years | 123.5 lb. (56.02 kg) | 67.0" (170.1 cm) |
| 16 Years | 134.0 lb. (60.78 kg) | 68.3" (173.4 cm) |
| 17 Years | 142.0 lb. (64.41 kg) | 69.0" (175.2 cm) |
How to get taller at 18?
Staying physically active is even more essential from childhood to grow and improve overall health. But taking it up even in adulthood can help you add a few inches to your height. Strength-building exercises, yoga, jumping rope, and biking all can help to increase your flexibility and grow a few inches taller.
Is 5.7 a good height for a 15 year old boy?
Generally speaking, the average height for 15 year olds girls is 62.9 inches (or 159.7 cm). On the other hand, teen boys at the age of 15 have a much higher average height, which is 67.0 inches (or 170.1 cm).
Can you grow between 16 and 18?
Most girls stop growing taller by age 14 or 15. However, after their early teenage growth spurt, boys continue gaining height at a gradual pace until around 18. Note that some kids will stop growing earlier and others may keep growing a year or two more.
Can you grow 1 cm after 17?
Even with a healthy diet, most people's height won't increase after age 18 to 20. The graph below shows the rate of growth from birth to age 20. As you can see, the growth lines fall to zero between ages 18 and 20 ( 7 , 8 ). The reason why your height stops increasing is your bones, specifically your growth plates.
